Open source intelligence (OSINT) is emerging as a formidable set of techniques for collecting and analysing information available on the Internet. At cyber securityOSINT, competitive intelligence and risk management, reveals potential security threats and vulnerabilities, monitors your e-reputation and informs your competitive strategy. Discover the OSINT tools and master this strategic discipline to stay one step ahead!

What is OSINT?
OSINT stands for Open Source Intelligence.. It refers to the collection, analysis and exploitation of information from publicly accessible sources. This allows users to gather and cross-reference data on individuals or organisations from a wide range of sources: social networks, websites, forums, databases, and many others.
It is important to note that OSINT is not limited to online information. It can also include data from physical sources, such as newspapers, books or public reports.
To be considered as OSINT information, it must meet three essential criteria:
- be obtained from a freely accessible source,
- be acquired legally,
- be available free of charge.
Cybersecurity professionals use it for ethical hacking, penetration testing and identifying external threats. But they are not the only ones.
Who is OSINT for?
OSINT is used by several categories of users and professionals:
- Intelligence and national security servicesThis is particularly true in the military and intelligence sectors, where it is used to gather strategic information.
- Businesses as part of business intelligence, to monitor the competition, identify market trends and make strategic decisions. They can also monitor their e-reputation.
- Cybersecurity specialists to identify potential threats and strengthen system security.
- Journalists and investigators to carry out investigations and check the veracity of information. Le Monde has a dedicated OSINT unit.
- The detailsto check its own digital presence and manage its e-reputation.
- International organizations and actors in the legal world : For example, the International Criminal Court uses OSINT to gather evidence.
What is OSINT used for?
If we confine ourselves to the field of cyber security, OSINT represents a goldmine of information that is potentially crucial to the security of organisations. There are several reasons for this:
- Threat monitoring OSINT enables cybersecurity managers to keep abreast of the latest threats, vulnerabilities and attack techniques discussed on specialist forums and social networks.
- Digital footprint assessment Using OSINT, professionals can assess their organisation's online exposure and identify sensitive information that could be exploited by malicious actors.
- Early detection of data leaks OSINT can help to detect data leaks quickly by monitoring dark web black markets and other platforms where this information could be for sale.
- Improving safety posture : By understanding how their organisation is perceived from the outside, the CISO can identify and correct potential weaknesses in their security infrastructure.
- Support for investigations In the event of a security incident, OSINT can provide valuable information for the investigation and attribution of attacks.
OSINT techniques and tools
The techniques
1. Passive collection
Passive collection involves monitoring and analysing publicly available information without interacting directly with the sources. This approach has the advantage of being discreet and minimising the risks of detection. Professionals can use social media monitoring tools (HootSuite or TweetDeck to follow specific hashtags), RSS feed aggregators, or monitoring platforms (Google Alerts to monitor mentions of a specific company or individual). Another widely used technique is to analyse the metadata of online documents (images, PDF, DOCX, etc.).
2. Active collection
Active collection involves direct interaction with information sources. This can include the use of advanced search engines (Google Dorkssearch in patent or trademark databases, etc.), the use of scanners (Shodan), of web scrapi techniquesng to extract data from websites, searching databases or Internet archives to find buried (hidden, deleted or old) information, or even taking part in online forums or discussion groups. Although more risky in terms of detection, this approach can provide more targeted and up-to-date information.
3. Data analysis
Once the data has been collected, professionals need to analyse it to extract usable information. Data analysis tools, visualisation tools (Painting, Power BI...), event timeline creation (TimelineJS...) and artificial intelligence (Perplexity, ChatGPT, IBM Watson...) can be used to identify trends, anomalies or hidden connections in the large quantities of data collected.
The tools
Hundreds of tools are freely available on the Internet. They can be divided into three categories:
Search engines
Of course, Google (through Google Dorks) and Bing are good tools for finding information. But specialised search engines give excellent results, depending on what you're looking for.
- Google Dorks (or Google hacking)
Google Dorks are Google's advanced search operators, which you enter in the search bar of the famous search engine. Here are some commonly used operators:- site: limits the search to a specific domain name
- filetype: searches for files of a particular type
- intitle: search for pages with a specific title
- inurl: search for pages with a URL containing a specific term
- intext: search for pages containing a specific text
For example:
- Find PDF files on a specific site :
site:example.com filetype:pdf
- Search for login pages:
intitle: "login " inurl: "admin "
TFind web pages containing lists of files and directories, which can reveal sensitive information accidentally stored in public spaces.intitle: "index of"
- Find files containing sensitive information:
filetype:xls intext: "username " OR intext: "password "
- Look for pages containing "login.php", which may reveal vulnerable login pages or authentication forms.
site:example.com inurl:login.php
Other specialist search engines:
- Shodan IoT: search engine specialising in Internet-connected devices (IoT) and IT systems. It allows you to find devices online and analyse their configurations. For example, you can identify insecure IoT devices.
- ZoomEye The Web Services Search Engine: a search engine that allows users to extract public data from exposed web services and devices. It finds IP addresses interacting with hosts, networks, open ports on remote servers, the total number of websites and devices hosted, and interactive maps of users accessing different devices.

Specialist departments
- Maltego The "data wall": an information visualisation tool that brings together data from different sources and displays it in the form of interactive graphs. Very useful for researching relationships between people or mapping a company's networks.
- SpiderFoot The Target Analyzer: this open source automated recognition tool gathers information from a variety of sources to produce a detailed profile of a target. In particular, it offers the possibility of obtaining and analysing IP addresses, CIDR ranges, domains and sub-domains, e-mail addresses, telephone numbers, user names and so on.
- Wappalyzer Security research: this very useful service enables security research professionals to quickly identify the technologies (CMS, frameworks, etc.) used on websites.
- TheHarvester This tool is used to collect information on domains, sub-domains, e-mail addresses and employees.
- Seon Digital Identity Check: this tool is used to check the digital identity of a person or organisation by assigning a risk score based on 50 different social signals. This makes it possible to confirm the validity of a customer's e-mail address or telephone number and to obtain further information about their digital footprint.
Specialised frameworks
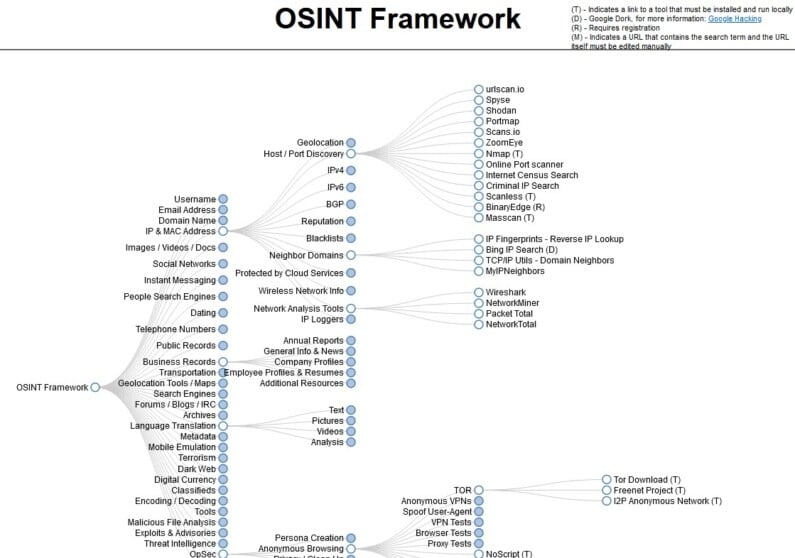
- OSINT Framework is an impressive collection of OSINT tools organised by category
Challenges and ethical considerations
1. Information overload
The massive amount of data available can quickly become overwhelming. According to one study, 61% of data teams feel overwhelmed by the mass of information they have to process. CISOs therefore need to develop effective strategies for filtering and prioritising relevant information.
2. Data reliability
Not all the information found via OSINT is necessarily reliable or up to date. This is why professionals need to develop an acute critical sense and implement rigorous verification processes to ensure the quality of the information used.
3. Respect for privacy
Although the information collected is publicly accessible, it must be used in compliance with data protection and privacy laws. Professionals must be particularly careful not to cross the line between legitimate information gathering and invasion of privacy.
4. Legal framework
OSINT must be used within a strict legal framework. In fact, investigators must ensure that their practices comply with the laws and regulations in force, in particular with regard to the collection and processing of personal data.
OSINT training to improve IS cybersecurity
OSINT is a powerful tool for cybersecurity professionals in their mission to protect their organisation's information systems. Incorporating it judiciously into your security arsenal is a strategic resource.
By providing a better understanding of the threat environment and the company's online exposure, OSINT helps to significantly strengthen the overall security posture. However, its effective use requires a considered and structured approach, taking into account the technical, ethical and legal challenges it raises.
This is why mastery of OSINT has become an essential skill for any professional wishing to excel in cybersecurity. ORSYS offers more than 170 international training courses and certifications in cybersecurity within its Cyber Academyto meet every need.





