With the upheaval caused by ChatGPT and its ilk, AI is putting businesses in a state of upheaval. This is an opportunity to go back to basics: what are the differences between an AI, the machine learning and the deep learning ? Think you know it all? Now's the time to put your knowledge to the test!

Just read an article about the prowess of ChatGPT or MidJourney to come across the terms artificial intelligence, deep learning and machine learning. Their definitions and meanings are sometimes confused and often misunderstood. Yet they refer to very distinct concepts.
AI, machine learning, deep learning - what are we talking about?
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the ability of a system to simulate human intelligence. The American pioneer of AI, Marvin Minsky, had a more precise definition: AI is "a science whose goal is to have a machine perform tasks that humans perform using their intelligence."
This covers a wide range of systems, from expert systems to chatbots, l'machine learningnatural language processing (NLP), the computer visionthe autonomous agentsThese include the use of computer models, neural networks and genetic algorithms (an optimisation method inspired by the process of natural selection).
Machine learning
Le machine learning (ML), or automatic learning, is a branch of artificial intelligence that enables computers to learn without having been explicitly programmed. This is the definition given in 1959 by one of its pioneers, Arthur Samuel.
Machine learning works on the basis of examples. It uses algorithms to statistically analyse data and identify patterns. These models are then used to predict results, gain a better understanding of the processes that generate the data or make decisions.
Its uses :
- Classification: classify files according to their content, detect anomalies on a production line, detect spam, etc.
- Regression: predicting a numerical value, useful for finding out how the weather or a share price is evolving.
- Grouping: grouping customers by persona and buying habits
- Search engines, recommendation engines...
- Conversational agents (chatbots)...
Deep learning
Le deep learning (DL), or deep learningis a subset of machine learning. It uses artificial neural networks (ANNs), algorithms inspired by the way the human brain works, mimicking the way neurons send signals to each other. These neurons are organised in interconnected layers with a certain level of depth (the deep of deep learning). Each level of depth helps to optimise and refine the accuracy of the results.
Les algorithmes de deep learning sont très adaptés à la problem solving complexes. Ils nécessitent un grand volume de données et par conséquent une très grande puissance de calcul pour les traiter.
Its uses image recognition (health, industry, etc.), machine translation (Google Translate, DeepL, etc.), voice recognition (Siri, Alexa, etc.), financial services (fraud detection, etc.), predictive analysisrisk assessment), self-driving cars, robotics (teaching robots to carry out complex tasks), etc.
Let's sum it all up with a sketch.
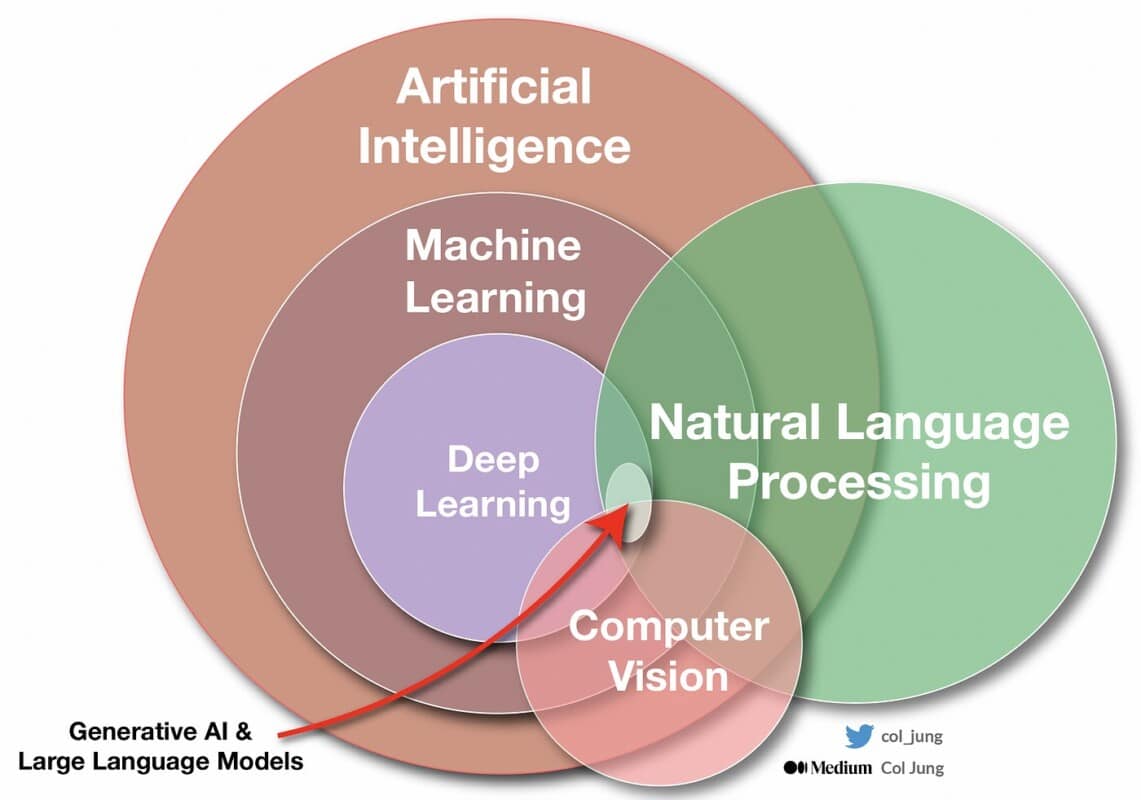
The differences between machine learning and deep learning
Types of learning: supervised, unsupervised, reinforced
Machine learning and deep learning algorithms need to learn from example data in order to adjust their parameterscalled training data sets (train datasets). Without training, artificial intelligence is nothing. The quality of the training determines the quality of the results. There are several types of learning: supervised, semi-supervised, unsupervised and reinforcement learning.
Supervised learning
Supervised learning involves one or more humans helping the computer by providing it with training data labelled with the correct answer to a question.
For example, is this email spam or not? Thanks to statistical analysis, the algorithm then understands which features enable it to classify these e-mails. As new e-mails are presented to it, it will be able to identify them and assign them a probability score as to whether or not they are spam. The human will be used to correct its errors during the learning process so that it can improve over time.
Unsupervised learning
Unsupervised learning applies when the answers we are looking for are not available in the dataset: the data is not labelled. The algorithm works without human intervention. It learns itself how to discover information from a set of data. Its results may be less accurate than supervised learning.
Unsupervised learning is used to :
- data clustering operations based on similarities or differences. For example, grouping bank customers according to their profile.
- association operations to identify relationships between variables in a data set.
Other types of learning
Semi-supervised learning consists of learning labels from a partially labelled dataset. The advantage is that this avoids having to label the entire training dataset. This is often the case when processing an image database.
Reinforcement learning consists of letting the computer learn from its experiences by means of a system of rewards and penalties if the action taken was a good or bad choice. The aim of the algorithm will then be to define a strategy that maximises its reward. The main applications for this type of learning are games (chess, Go, etc.) and robotics.
Types of data: structured and unstructured
Another major difference between machine learning and deep learning is the type of data input to the dataset.
Le machine learning deals with structured datadata organised according to a predefined model, which can be easily indexed like a table or a database, as well as unstructured dataUnstructured data is data that does not follow a particular model. Unstructured data can be text, images, video, audio, etc.
Le deep learning is used to process and analyse unstructured data.
Let's summarise in a table
Differences between Machine Learning and Deep Learning
| Features | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Type of learning | Supervised or unsupervised | Supervised, semi-supervised or by reinforcement |
| Human intervention | Strong to medium | Low |
| Type of input data | Structured or unstructured | Unstructured |
| Type of output data | Numerical values | Numeric values, text, image, voice, video... |
| Volume of data required | Low to medium (thousands) | High (millions, even billions) |
| Importance of data quality | Very important | Important |
| Training time | Short | Long |
| Computing power required | Low to medium (CPU) | Strong (GPU) |
Finally
AI, machine learning and deep learning are three distinct elements. AI is the discipline and, by extension and metonymy, the products or services based on AI: Siri, ChatGPT, the AI of autonomous cars, theRadiology AI that detects more and more cancers...
Machine learning and deep learning are two automatic learning techniques used by AI. However, they have different uses. Machine learning algorithms process quantitative and structured data, whereas deep learning algorithms process unstructured data such as sound, text or images.
And what are Generative AI such as ChatGPT, Bard, DALL-E or MidJourney? They produce text, images or code, or are even multimodal, and are based on LLM (large language models). They use deep learning and neural networks to process billions of unlabelled texts.
If you too would like to create your own AI models, learn how to work with AI or simply find out more about this revolution, we offer you the following options some sixty seminars and training courses to take you into this exciting world!





