Following the advent of BIM, professionals in the construction sector need to familiarise themselves with the concept of lean management. Originating in industry, this approach to production management is gradually gaining ground in the construction sector. The key aim is to reduce wastage of time and materials. So how do BIM and lean complement each other? And how does lean provide a practical response to the problems encountered in BIM projects? Haïssem Ben Achour, an engineer specialising in BIM, explains.

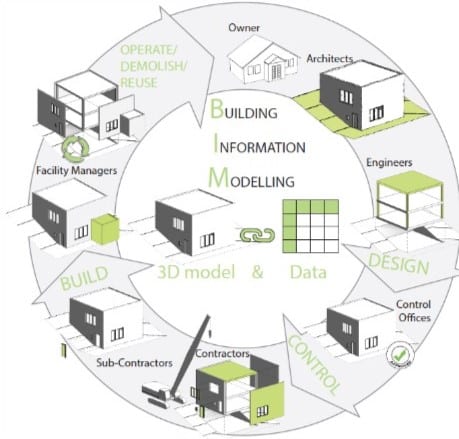
BIM (building information modelling) is a technology for creating a 3D digital model of a building, incorporating all the information required for its design, construction and management.
Lean is a project management method that aims to eliminate waste and optimise processes. It places the emphasis on collaboration, communication and continuous improvement.
The contributions of BIM for construction
In 2022, the results of the 2ᵉ edition of the barometer on the use of digital and BIM by construction professionals were clear-cut. For 48 % of industry players, BIM is a strategic issue for their business. That's up 11 points on the previous edition. According to the same survey, 66 % of those who work with BIM are convinced of its usefulness and importance, and 17 % have taken action to promote BIM within their company.
BIM has revolutionised working practices and methods in the construction industry.
Here are the main benefits of BIM for professionals in the sector.
Improved collaboration
BIM enables the various parties involved in a construction project (architects, engineers, contractors, etc.) to work on a common platform. This helps to resolve problems and reduce errors and delays.
3D visualization
Thanks to BIM, professionals can better visualise and understand the project, making it easier to make decisions and communicate with customers.
Data management
BIM centralises project information in a single database, thereby reducing construction-related risks. These risks mainly concern the loss of data. Shared by users, this data is stored everywhere and nowhere on the cloud or on physical servers.
Simulation and analysis
BIM makes it possible to carry out advanced simulations and analyses, such as energy analysis, daylighting simulation and traffic flow simulation, optimising design and decision-making.
Building life cycle management
BIM makes it possible to manage the stages from design to construction, including operation and maintenance. The result: optimised costs, improved energy efficiency and a longer lifespan for the building.
Example
BIM will help optimise the maintenance and management of facilities after the Paris 2024 Olympic Games. It will be possible to track necessary maintenance and repairs to facilities, extending their useful life and reducing maintenance costs in the long term.
Is BIM a lean solution?
The combination of lean and BIM provides a solution to the problems encountered in BIM projects. Thanks to this "winning duo", it is possible to :
- Reducing waste
- Improving collaboration
- Optimize processes
- Reducing errors and risks
Lean identifies unproductive activities and eliminates them. By using BIM, it is possible to visualise the project before it is built, to detect errors and potential problems and to correct them before they become waste.
Lean also encourages collaboration between the parties involved in a project. Using BIM, information and models can be shared easily, encouraging collaboration and coordination.
Lean also analyses existing processes and improves them to make them more efficient. BIM models and simulates the various stages of construction, in order to identify the stages that need to be optimised and to anticipate potential problems.
Finally, lean puts the emphasis on quality and error prevention. Using BIM, it is possible to detect errors and inconsistencies in the digital model, enabling them to be corrected before construction.
BIM can be described as a lean solution in that it helps to eliminate waste and optimise construction processes.
Good practice in a BIM project
Accuracy and consistency
To achieve a greater degree of precision and consistency in the use of BIM, here are a few best practices to follow:
- Standardization: use standards and protocols to guarantee the consistency of models and data.

In a way, BIM is the digital avatar of the physical building. Each component of the real building is represented by an equivalent digital object in a database that uses an ISO-certified exchange format called "IFC" (industry foundation classes). This is linked to a standardised dictionary of product data, the data dictionary (bSDD).
- Training and awareness: A good understanding of BIM means you can work more accurately and consistently.
An example of training: introduction to BIM with Autodesk Revit
BIM technology is changing the way buildings are designed, constructed and used. This course will help you understand the main benefits of BIM and help you better manage your design projects, using Autodesk Revit modelling software.
- Quality control : checks for compliance with standards and collision tests to detect conflicts.
Examples of model checking and collision detection software:
MagiCAD Add-in, Trimble Connect, BIM Vision, Solibri Model Checker...
- Close collaboration : share information in real time.
- Use of advanced tools : These tools automate tasks, optimise design and guarantee data consistency.
There are several examples of BIM automation functions available in the industry. The best-known example is the combination of Revit and its integrated Dynamo programming interface.
In the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, the glass cladding of the Cité du Vin in Bordeaux was a real challenge, which was met thanks to BIM and Dynamo.
Facilitate communication
The aim is to streamline communication and exchanges between the various trades involved in a construction project. How can this be achieved?
- Use a BIM collaboration platform
- Organize regular meetings
- Define responsibilities and roles clear
- Use a common language and understandable
- Promote transparency to understand the constraints and needs of other business lines
- Encourage active participation, individual commitment and responsibility
- Use appropriate communication tools: 3D modelling software, task management tools, instant messaging platforms, etc.
Examples of 3D modelling software
Autodesk: AutoCAD, Inventor...
Dassault : Catia, SOLIDWORKS...
Bentley: MicroStation
Controlling costs and deadlines
In a construction project, controlling costs and deadlines can be complicated. Following these steps can help.
- Detailed planning
- Precise cost estimates
- Regular monitoring of costs
- Rigorous resource management
- Risk management
- Communication and coordination
- Quality control
- Use of BIM
What lean tools and methods are needed for BIM projects?
How can you rethink and control the change process using lean methodologies? Here are a few steps to follow.
- Identify the objectives of the change
Objective: improve efficiency, reduce costs, improve quality, etc.
- Involve stakeholders
The active participation of employees, customers and suppliers is essential if change is to succeed.
- Analyze existing processes
Identify value-added and unnecessary activities.
Use lean tools such as value-stream mapping to visualize and understand current workflows.
- Eliminating waste
Waste can include waiting times, unnecessary movements, excessive stock, defects, etc.
Use lean tools such as 5SKaizen and Just-in-Time to reduce waste.
- Implement continuous improvements
Implement a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging employees to put forward ideas for improvement.
Use lean tools such as Kaizen to facilitate this continuous improvement process.
- Measuring and monitoring results
Set up key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure and monitor the results of the change.
- Communicate and train
Ensure that all employees understand the objectives of the change and are trained in the new working methods.
- Adapt and iterate
Be prepared to adapt and iterate the change process according to the results obtained and feedback.
Example of BIM deployment in an E+C project
APSARA is an E+C- (Positive Energy (E+), Carbon Reduction (C-)) labelled residence located at the heart of the ZAC Ovalie, Montpellier's new eco-district. The aim: high energy performance and maximum reduction in carbon emissions.
The E+C- approach using BIM is based on a thermal calculation carried out by a design office, using the digital model. Normally, the fluid and thermal engineer has to retrace the architectural model in the dedicated software to carry out the calculation. For this project, the BIM approach we have put in place has streamlined exchanges between the design office and the architect. The architect was able to produce a model that met the needs of the design office, and the E+C- calculation was carried out directly from the architectural model.
The combination of lean and BIM represents a significant opportunity to improve productivity and efficiency in the construction sector. In the coming years, lean and BIM will evolve even further thanks to artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things.
This development promises even more efficient, sustainable and customised construction processes, tailored to the specific needs of each project and customer.
However, despite the obvious benefits, full adoption of these methodologies requires: adapting to regulatory changes, training the workforce in the new technologies and promoting a culture of innovation and collaboration within the industry.





