Industry is undergoing radical change, driven by the wave of Industry 4.0. The integration of artificial intelligence and robots is profoundly reshaping industrial processes, promising significant productivity gains. How are French companies integrating these technologies in practice? What are the key figures and use cases that illustrate this transformation?

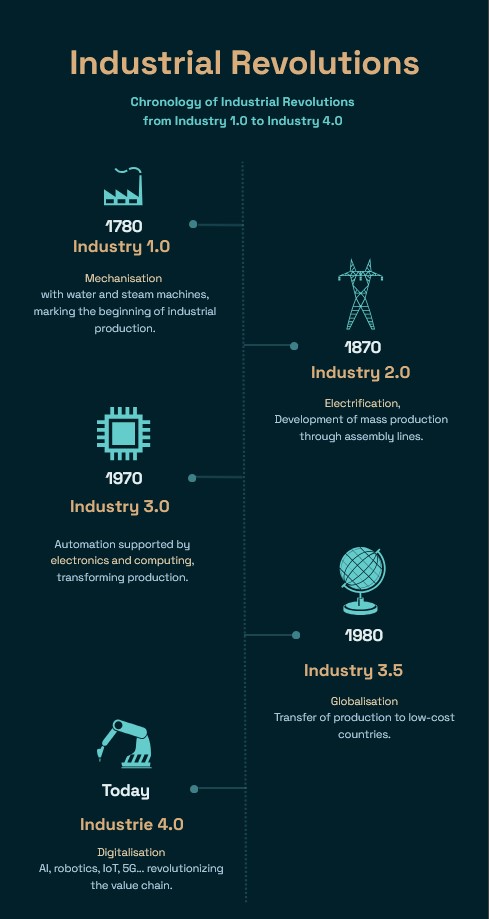
Industry 4.0: an accelerated technological transformation
Industry 4.0, often referred to as the "fourth industrial revolution", is based on the integration of digital technologies throughout the industrial value chain. According to the Industry 4.0 Barometer 2024 from WaveStone, 66 % of French companies declare themselves mature in the adoption of 4.0 technologiesThis represents a significant increase of 8 % on the previous year.
AI and robotics are at the heart of this transformation, playing a key role in the future. role crucial to improving performance.
AI, driving optimisation in industry 4.0
AI is establishing itself as a pillar of Industry 4.0, enabling advanced automation, the development of new technologies and the creation of new jobs.predictive analysis and process optimisation. Companies that adopt it are looking to improve product quality by analysing production data and anomaly detection. Image analysis for quality control is performed by AI, which identifies defects and non-conformities faster and more accurately than the human eye.
AI also makes it possible to reduce equipment downtime by anticipating maintenance needs thanks to the predictive maintenance. By analysing machine sensor data, AI can predict breakdowns and maintenance requirements, reducing downtime and repair costs.
L'Industrial IoT and AI enable data to be analysed in real time, reducing downtime by an average of 30 % thanks to early diagnosis. At AirbusThis technology has reduced maintenance costs and optimised machine availability.
Finally, it increases flexibility and customisation in production by adapting processes in real time according to demand.
Robots, from automation to collaboration
Robotics, meanwhile, is no longer limited to repetitive tasks. The rise of collaborative robots (cobots) opens up new perspectives:
- Improving working conditions the cobots can take on tasks that are arduous and dangerous for human operators, improving safety and quality of life at work. For example, Renault uses cobots in its factories to speed up the assembly of parts while reducing employee fatigue.
- Increased productivity cobots work alongside human operators, enabling more effective collaboration and increased production.
- Improved flexibility cobots are more easily reprogrammed and adapted to different tasks than traditional robots, offering greater flexibility in production.
Use cases for robots in industry
- Assembling and handling parts cobots can assist operators with precision assembly tasks and the handling of heavy or fragile parts. This is the case at MGA Technologies. This medical device manufacturer has integrated collaborative robots to achieve greater manufacturing precision and a reduction in rejects of 15 %.
- Quality control Robots equipped with cameras and sensors can carry out visual inspections and dimensional measurements to guarantee product quality.
- Logistics and handling the autonomous mobile robots (AGVs and AMRs) can transport goods and materials around the plant, optimising logistics flows. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are now ubiquitous at Amazon which uses them to manage its warehouses and speed up order processing.
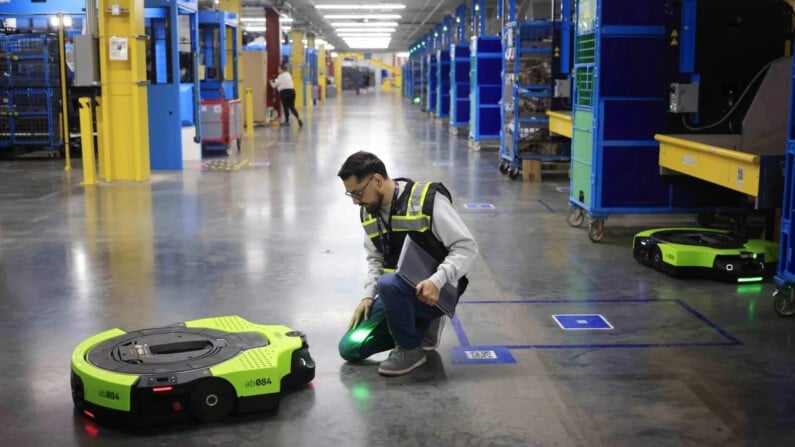

It can lift up to 560 kg of products. ©Amazon
Performance drivers: data and automation
Data is the foundation of Industry 4.0. Mastering the data management is on the rise: 77 % of manufacturers consider that they manage their data wellcompared with 53 % the previous year, again according to the WaveStone 2024 barometer.
All these data enable l'growing use of digital twins These virtual replicas can be used to simulate production lines and facilitate the design of products before they are actually manufactured. The Group's SafranFor example, it uses this technology to optimise its aircraft engines, reducing development time by 20 %.
Industry 4.0: environmental and sustainability issues
Industry 4.0 is also playing a key role in the ecological transition, particularly when it comes to energy optimisation. 69 % of companies are adopting energy management solutions, reducing their consumption by up to 20 %, according to the WaveStone 2024 study.
Additive manufacturing is also making its contribution: 3D printing, adopted by General Electric makes it possible to manufacture complex parts or spare parts while minimising waste. The Groupe SEB also uses 3D printing to manufacture certain spare parts on demand or to produce prototypes.
Persistent challenges for SMEs
Despite this progress, many obstacles remain, particularly for SMEs:
- Insufficient technological infrastructure 79 % of companies consider their infrastructure to be inadequate, which is holding back the adoption of new technologies.
- High cost of processing The initial investment is high, combining expenditure on hardware, software and training. For example, the deployment of an MES management system can cost several hundred thousand euros.
- Cybersecurity Increasing interconnection exposes companies to new risks cyber attacks. In 2024, attacks against industrial infrastructures increased by 35 %, requiring the rapid adoption of strategies such as the Zero Trust.
Training: an essential lever
The transition to Industry 4.0 requires specialised skills that are specific to the sector and therefore rare. Players like ORSYS are training employees in the key technologies of robotics, AI, IoT and cybersecurity. Our expert Serge Gueguen explains why choose ORSYS to support your development in Industry 4.0.
Conclusion
Driven by AI and robotics, Industry 4.0 offers considerable opportunities for French industry. By adopting these technologies, companies can boost their performance, flexibility and competitiveness.
However, the success of this transformation will depend on companies' ability to overcome the challenges associated with cybersecurity, technological investment and talent training. Concerted efforts between the public and private sectors will be essential to ensure a successful transition to a high-performance, resilient and forward-looking French industry.





