Does immersive learning represent the future of training? Although it is too early to say, this technology is already revolutionizing learning methods thanks to virtual reality. But for which professions and skills is immersive learning most beneficial? What are its practical advantages and limitations? The point with Gauthier Lamothe, specialist in pedagogy.

Overview of what immersive learning can bring to training!
Immersive learning: definition
Immersive learning is a generic term. It characterizes any type of training using technology to give the learner the impression that he or she is indeed present in a virtual situation. Nowadays, it mainly refers to learning skills via virtual reality. Or VR for virtual reality. But, in a broader sense, this covers other related practices, such as augmented reality.
Immersive learning: what concrete impacts on learning?
Practice in real conditions is obviously an irreplaceable asset for integrating the reality of a profession. However, real conditions are sometimes difficult to implement during training. This is why practicing periodically in real conditions and regularly in virtual conditions has many advantages.
First, any repeated practice creates neural pathways in the brain and maintains them. In other words, skills are acquired and anchored through training.
For example :
- educate yourself to spot certain visual details
- repeat a procedure in order
- practice certain verbal refrains to defuse a conflict
- practice raise a counter-objection in the world of sales
Thus, VR allows you to forge all the reflexes that will be used in reality. Furthermore, in some contexts the difference with reality is minimal and the number of training sessions is much higher. Immersive learning therefore improves the anchoring of knowledge among learners, whatever their sector of activity (or almost).
Virtual reality gives learners the rather pleasant feeling of “being there”, in situations that are complicated to implement in the real world.
It becomes possible to update knowledge regularly in rare situations that cannot be provoked voluntarily. This is a key advantage of VR because learning occurs via cycles of forgetting and updating.
Finally, immersive learning technologies, in particular VR, make it possible to focus on a specific situation, freeing oneself from the preceding and following context.
Some concrete examples
On a very practical level, it becomes possible, for example, to:
- rrepeat a maneuver 50 times in one morning, without the need to set up a teaching environment each time
- isolate certain tasks from each other even though they could not normally be carried out separately
Example :
In some laboratories, safety standards are draconian and the use time of certain products is very short. Chemical elements are unstable or radioactive, often dangerous, and disintegrate quickly. For safety reasons, only one operator at a time can insert their hands into the gloves integrated into the handling box. In addition, he must complete the procedures in one go. Therefore, a trainer does not have enough time to comment on the steps and emphasize details.
- provide participants with highly engaged role play partners
Example :
During conflict management training, it can be difficult to have partners capable of improvising and portraying a character with conviction. Immersive learning then allows you to practice certain delicate interactions. Indeed, coupled with generative artificial intelligence like ChatGPT, immersive learning has potential to explore!
Also discover the article: ChatGPT: what uses in training?
Immersive learning and virtual reality: use cases in training
Virtual reality is beneficial for developing numerous skills, often linked to the specificities of a profession.
Physical inaccessibility
Example: manipulations carried out by technicians having to squeeze into a confined space. These may involve cleaning, repair or maintenance operations in wells, silos, pipes, etc. In this context, training numerous technicians with virtual reality is of certain interest, both in terms of budget and space. physics required.
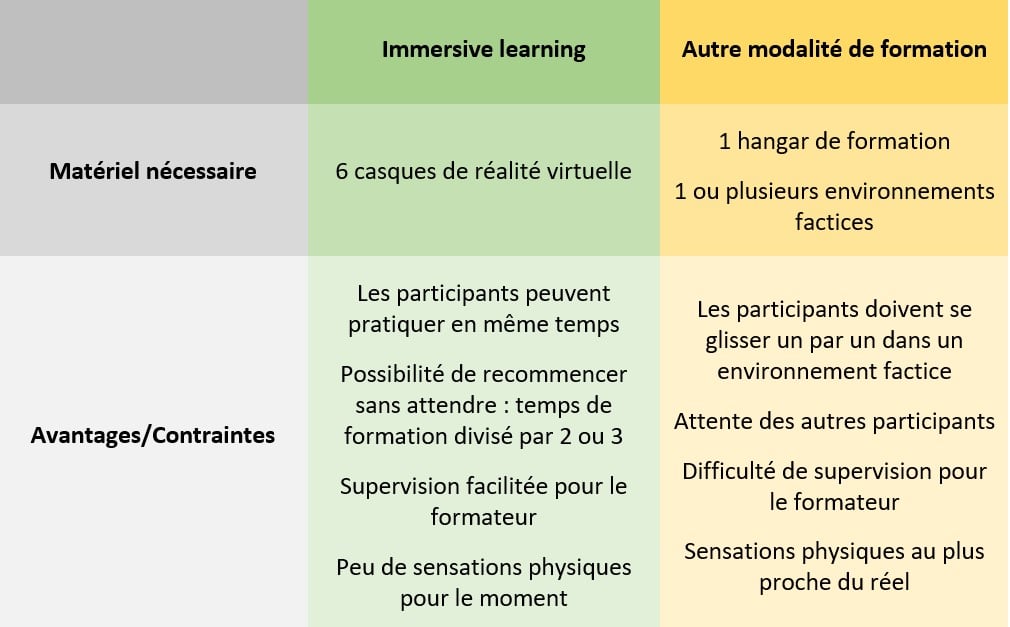
Here, for the training of six specialized maintenance technicians :
Ethics
In the medical field, learning certain gestures requires many hours of practice. Virtual reality then facilitates learning comfort and allows for mistakes. And making mistakes is essential for learning…
Convenience
Example: in the sector of climate engineering (large industrial air conditioners).
Following training, one of the participants indicates that virtual reality is ultimately the most useful in the use of 3D models of their machines. In fact, the new technicians in training put on a helmet and can then analyze each mechanical part from every angle, in three dimensions, and dismantle each part down to the screw.

To note : Immersive learning, on the other hand, is little used in the world of software since it is already an infinitely malleable environment.
Immersive learning: what equipment?
In the world of VR, the hardware used will typically be a headset. Either a high-end headset with its own sound and image system, or a headset into which you slip a mobile phone. This tool can also be combined with screens or tablets so that participants can watch the progress of a fellow student.

In some cases it is useful to practice video duplication. This practice consists of reproducing the trainer's gestures in real time. The trainer then wears a camera connected to the participants' phones (if there is the possibility of installing a mobile application). Otherwise, the camera is connected to tablets provided for this purpose.
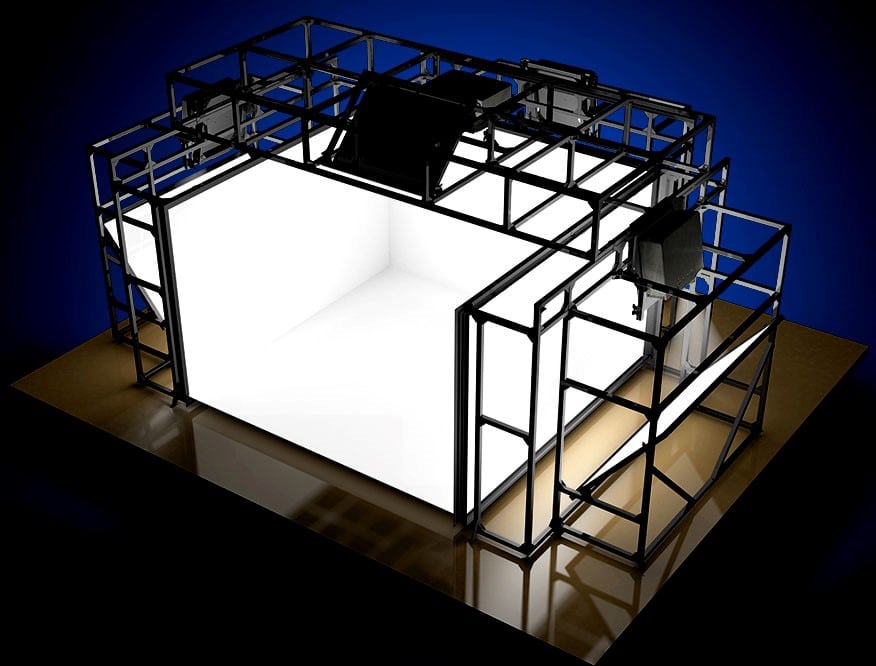
When participants need move in a 3D space, We are talking about immersive room. The CAVE VR system or the AET Zone are examples of already proven solutions, but whose custom installation requires a significant budget. Example: for motion detectors, from €20,000 to several hundred thousand euros. Certain technologies sometimes contain objects and physical stimulations (currents of hot or cold air, odors). This type of training concerns first aid and interventions in degraded conditions with teamwork (fire, landslide, etc.).
Immersive learning: obstacles, limits and challenges
The worst reason to use immersive learning is prestige.
Good technology is the one you don't see !
The use of VR must be motivated by improving the user experience for learners. But on what criteria should we measure it?
Performance indicators
Three performance indicators stand out.
- Anchoring knowledge
- The ability to solve problems
- Training time
In very large companies, it is easy to choose metrics and run tests.
Example 1:
Compare information retention in a group of employees benefiting from immersive learning and in a group not using it. This is also the case of a famous American supermarket chain which has the firepower necessary to conduct this type of test. Virtual reality has increased performance so much that this chain now has VR training centers dedicated to supply chain and sales.
Example 2:
Another American company, a leader in the fried chicken sector, also has training centers in the United States.
VR allows it to train operators to cook fried chicken in 10 minutes instead of 25, while avoiding wasting raw material.
According to a study by Capgemini Research Institute, 82 % of companies that have implemented immersive learning consider that virtual reality either met or exceeded their expectations. Employees who benefit from it ask for more training. And their performance is better.
Exploit data
Participants' interactions with this or that element of the simulation are recorded in an automated log. This allows you to identify friction points in training and improve it.
Example :
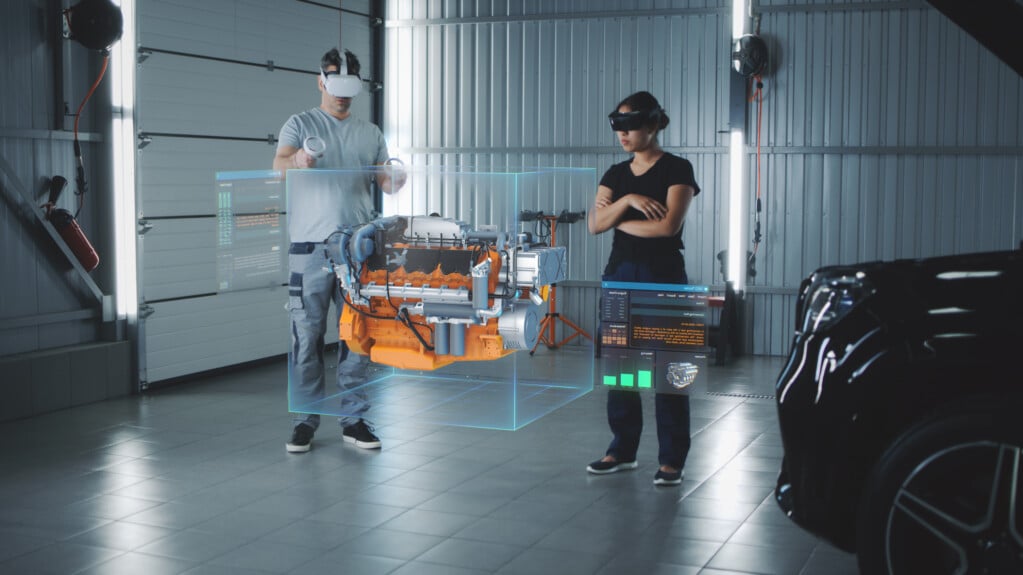
With HoloLens, a truck manufacturer improved engine quality control training thanks to augmented reality which gives operators real-time access to decision support tools
For small and medium-sized companies, it is appropriate to ask yourself at what scale immersive learning is profitable, both in terms of budget and training time. The challenge may be choosing a partner providing data analysis. This is to improve the quality of training without exploding costs by handling all parameters internally.
In conclusion, immersive learning tends to position itself as an essential training modality. As big data and artificial intelligence become more widely available, its solutions are becoming more and more accessible. By integrating user experience and gamification, immersive learning will further improve the quality of training.


