AI is entering a new era: that of the autonomous agents ! Imagine AIs that reason, plan and act. They manage your diary, answer your e-mails, automate complex tasks and interact with your tools to execute workflows. This could radically change your day-to-day business and personal life. Which tools should you choose? How can you use them to your advantage? Dive into the world ofAgentic AI !

Some two and a half years after the ChatGPT shockwave, artificial intelligence is taking another major step forward. After the Generative AI capable of creating content (text, images, code), such as ChatGPTGemini or CopilotThis is the age of AI agents.
Their fundamental difference: they don't just wait for an instruction to generate a response, they act. An AI agent can interpret an objective set by a human, break it down into logical steps, search for information (on the web or elsewhere), reason about the information gathered and drive various software tools (surfing the web, sending an email, interacting with an API, executing code...) in order to carry out its mission autonomously. To distinguish them from other AIs, we speak ofAgentic AI.
Industry leaders are in unison:
- Sam Altman (OpenAI) 2025 will be the year of AI agents
- Bill Gates Agent is going to revolutionise IT, like the switch from commands to icons".
- Jensen Huang (NVIDIA) The era of AI agents is a multi-trillion-dollar opportunity".
These systems represent a significant advance, promising to radically transform the way we work and interact with technology. But what exactly are they, where do they come from and what real impact will they have?
What is an AI agent?
An artificial intelligence agent is a system or program capable of performing tasks autonomously on behalf of a user or another system, by designing its own workflow and using available tools.
This distinguishes them from chatbots which simply generate content in response to instructions, and traditional software which performs tasks determined by its developers. AI agents have the ability to choose independently, without explicit instructions, the best actions to take to achieve these objectives.
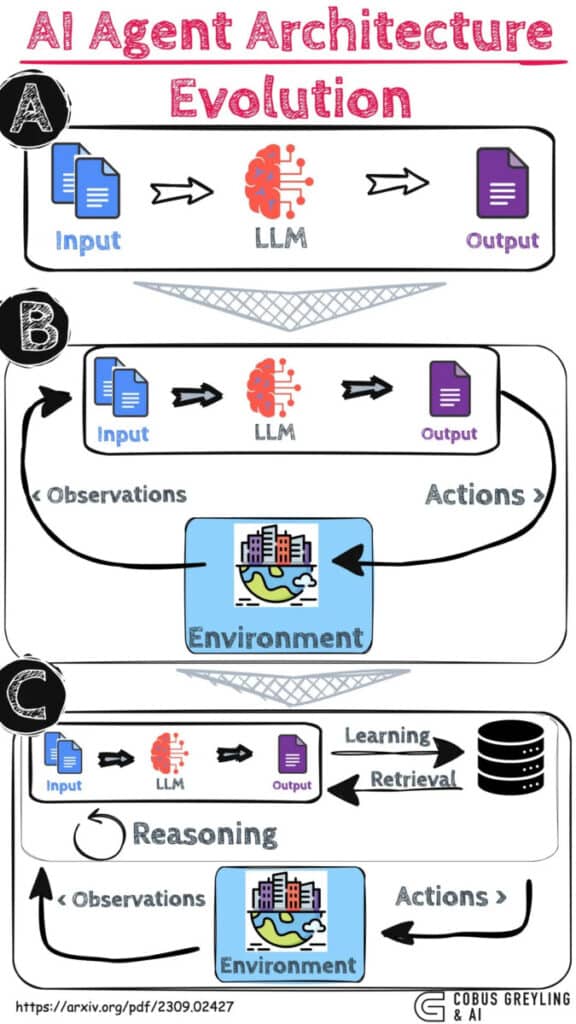
Differences between AI and LLM agents
It is crucial to differentiate AI agents from major language models (LLM) and other conventional AI systems.
LLMs, like ChatGPT, work mainly on the basis of the data on which they have been trained. Their knowledge is therefore limited to this data. They generally perform a single inference or prediction based on the user's query. Unless explicitly implemented, there is no management of session history or ongoing context (such as chat history).
Conversely, agents extend the capabilities of language models using tools to access information in real time, suggest actions in the real world, plan and carry out complex tasks autonomously.
They manage a session history (such as chat history) to enable multi-turn inference/prediction based on user requests and decisions made in the orchestration layer. The agent operates cyclically until it reaches its goal. An LLM generates, an AI agent acts.
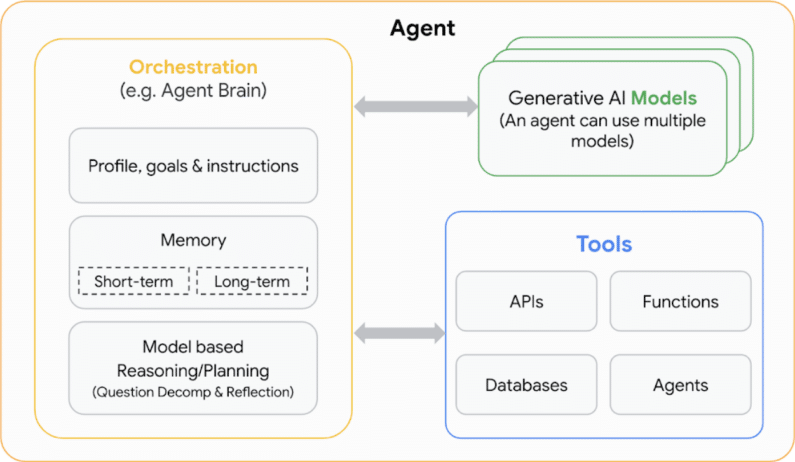
LLMs are the brains of agents
At the heart of AI agents are often LLMs, which provide sophisticated natural language understanding and generation capabilities.
Agents can use one or more language models to decide when and how to move from one state to another, and to use external tools to perform many complex tasks that would be difficult or impossible for the model alone.
However, the real innovation lies in the way these models are augmented with agentic capabilities. Agents are like layers on top of language models that observe and collect information, provide input to the model and together generate an action plan.
Are personalised GPTs AI agents?
It depends. A custom GPT created via the OpenAI GPT platform is basically a specialist LLM with specific instructions and knowledge.
If it simply answers questions based on its data, it is not an agent. However, if this custom GPT is configured with 'Actions' that allow it to interact with external APIs (search the web, connect to a customer database, send an email via Zapier), then it acquires agent capabilities.
It can perceive (via the API), reason (LLM) and act (via the API). The frontier is therefore defined by its ability to act on its environment beyond the simple generation of text.
Examples of the use of AI agents
AI agents are beginning to be integrated into various professional fields:
IT and development
- Task automation : code deployment, systems monitoring, incident management.
Examples of tools/platforms : frameworks such as AutoGen (Microsoft Research) or CrewAI allow teams of agents to be created for complex tasks (development, testing). AIOps platforms integrate agentic capabilities for proactive problem resolution. GitHub Copilot Workspace (GitHub/Microsoft) is evolving into an agent capable of planning and executing development tasks based on a natural language description.
- Systems monitoring and maintenance AI agents monitor IT infrastructures in real time to proactively detect and resolve anomalies, thereby improving system reliability.
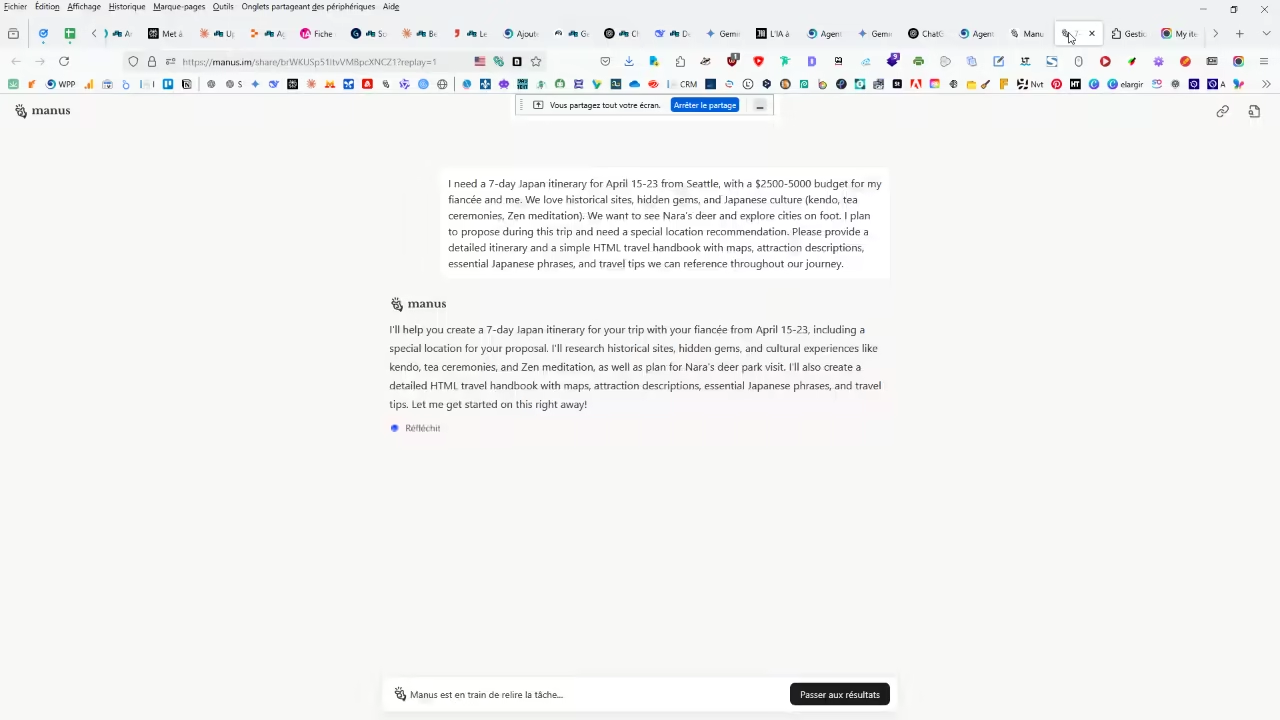
The star of the agents : Manus
Launched in March 2025 by Chinese start-up Monica, Manus is the embodiment of the autonomous agent revolution. It presents itself as the first autonomous general-purpose AI agentIt can plan, think and execute complex tasks without continuous human supervision.
It carries out tasks from A to Z (financial analysis, CV analysis, report generation, web development), and works asynchronously in the cloud: it continues even if the user disconnects.
A central "executing agent" coordinates specialist sub-agents (planning, research, code) to break down complex tasks.
Example: for a property search, it analyses prices, crime and weather trends.
A side window displays the Manus computer: showing each stage of the process (web browsing, document sorting, etc.), allowing human intervention if necessary. Sessions can be replayed for debugging or team sharing.
Marketing
- Campaign management : content creation, advertising bid optimisation, performance analysis, audience segmentation.
Examples of tools : platforms such as HubSpot, Salesforce or Microsoft Copilot for Marketing incorporate AIs that automate certain tasks and analyses, acting as assistants. Specialised agents could analyse trends in real time and dynamically adjust advertising campaigns on Google Ads or Meta. Tools such as Jasper (Jasper AI) can be orchestrated by agents to generate large-scale variations in content.
Executive assistants / Administrative staff
- Complex diary management : making appointments with several participants, booking trips, managing e-mails (sorting, standard replies, follow-up).
- Drafting e-mails and documents
- Text translations
- Meeting minutes...
Examples of tools :
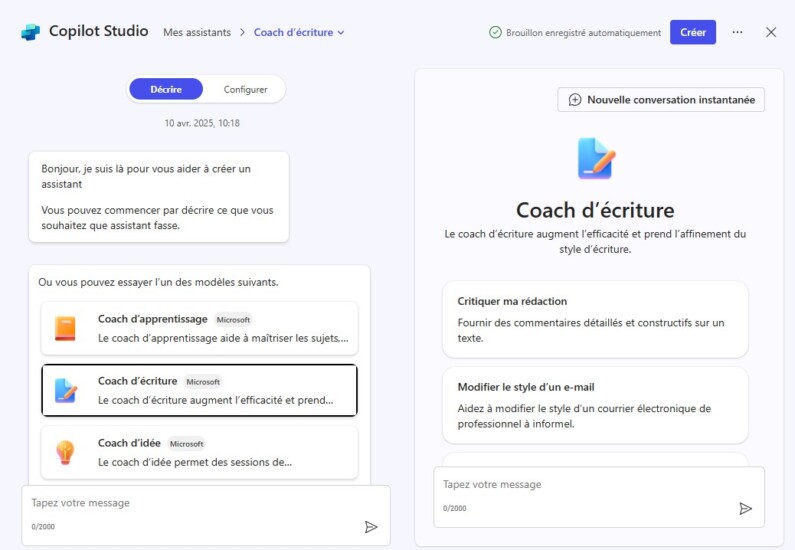
Microsoft Copilot Studio Copilot Studio: integrated into the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, Copilot Studio enables the creation and customisation ofconversational agents agents. These agents can interact with emails, calendars and documents, using predefined templates or customised agents to suit your specific needs.
Google Agentspace with Gemini Google Agentspace serves as a platform for deploying personalised AI agents, increasing employee productivity by automating complex tasks via a simple command. These agents can be adapted for various departments such as marketing, finance or human resources, facilitating processes such as content authoring, research and the automation of repetitive tasks.
Operator by OpenAI Operator: launched in January 2025, Operator is an artificial intelligence agent capable of interacting autonomously with web browsers to perform various administrative tasks. It can fill in forms, place online orders and schedule appointments, helping to automate repetitive tasks and free up time for higher added-value activities.
Human resources
- Recruitment : Screening CVs, scheduling interviews, answering frequently asked questions from candidates.
- Onboarding : Automated document dispatch, planning of initial training sessions.
Examples of tools : numerous Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) such as Raise or Greenhouse use AI for sorting. HR chatbots (often based on LLMs but able to trigger actions) act as first-level agents for employees.
Management
- Decision support AI agents provide managers with predictive analysis and data-driven recommendations, facilitating strategic decision-making.
Example of a tool : AutoGPT. This open source agent assists managers by automating complex tasks and providing in-depth analysis for decision-making.
Will AI agents replace humans?
This is the most debated question. The answer is nuanced. AI agents will very probably automate many tasksThis is particularly true of repetitive, rule-based tasks or those involving the rapid analysis of data. Some jobs that consist mainly of these tasks could be processed or reduced.
According to a report by UiPath, 90 % of IT leaders believe their business processes could be improved by agentic AI. The most anticipated benefits include increased automation (55 %), better problem solving (53 %) and greater accuracy with fewer errors (53 %). Some even envisage managing AI agents as employees, integrating them into hybrid teams made up of humans and AI working together.
However, they are unlikely to replace humans on a massive scale in the short to medium term for a number of reasons:
- They lack deep creativity, emotional intelligence, complex critical thinking and physical dexterity (for non-numerical tasks).
- They require human supervision, configuration, maintenance and exception management.
- New jobs will emerge around AI: AI agent manager, AI ethicist, specialist prompt engineer, AI trainer, etc.
- Their true potential often lies in theincrease human capacity, freeing up employees for higher value-added tasks (strategy, complex customer relations, innovation).
The future of work is probably moving towards a human-agent collaborationwhere everyone focuses on their strengths. The major challenge will be to adapt skills and manage this transition ethically.
In conclusion, AI agents represent a major development in artificial intelligence. They are no longer simple analysis or generation tools, but actors capable of autonomy and initiative in the digital environment. Their gradual integration into businesses promises considerable efficiency gains, but also raises technical, economic and ethical challenges that we will need to address collectively if we are to exploit their full potential responsibly. We are only at the beginning of this agentic revolution.




