EBIOS, ISO 27001 or ISO 27005 : These three approaches are used to identify, assess and control the threats to your IS. Which one should you choose? Which is best suited to your organisation? Between risk mapping, impact analysis and regulatory compliance, find out how to anticipate incidents and strengthen your organisation. resilience.

Managing the risks of cyber security has become a priority for organisations of all sizes, in the face of the increasing number of cyber attacks and their potentially devastating impact.
To structure their approach and protect themselves against these threats, a number of frameworks and methods are available to organisations, each with its own specific features, advantages and limitations. Among the most widely recognised are EBIOS Risk Manager (EBIOS RM), as well as ISO 27001 and ISO 27005.
Although distinct, these three approaches converge towards the same objective: securing information systems, protecting people and protecting the environment. sensitive datato ensure business continuity and preserve the organisation's reputation.
EBIOS Risk Manager: the tried and tested French method
Created over 25 years ago by theANSSIThe EBIOS method (Expression des Besoins et Identification des Objectifs de Sécurité - Expression of Requirements and Identification of Security Objectives) is distinguished by its pragmatic and iterative approach.
EBIOS RM is structured around five workshops that guide the organisation in analysing and dealing with digital risks. It encourages a detailed analysis of the organisation's ecosystem. It includes partners, suppliers and customers, in order to identify potential threats and map out the risks to which they are exposed. vulnerabilities structure.
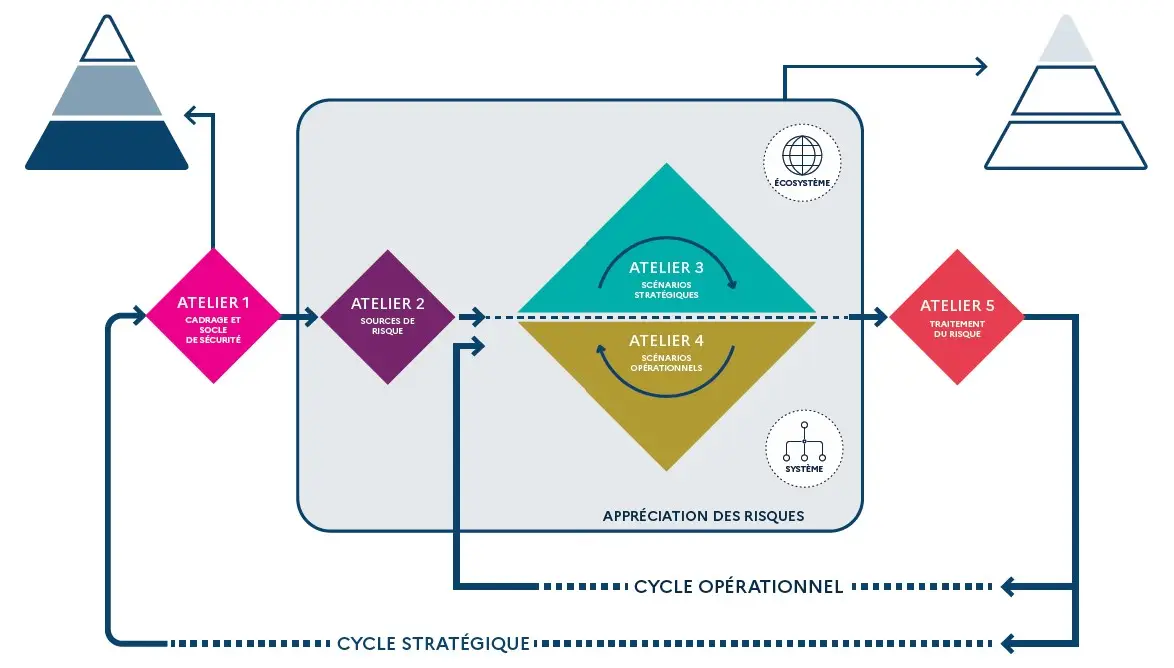
One of the strengths of RM EBIOS lies in its ability to combine a compliance-based approach for generic risks and a scenario-based approach for more specific, targeted risks.
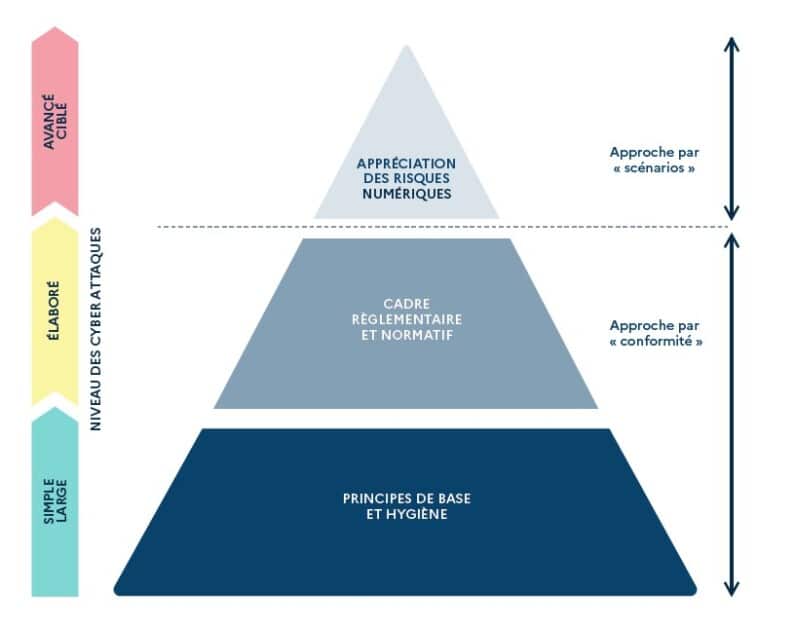
For common risks, RM EBIOS relies on standard security reference frameworks, such as the ANSSI guides or ISO 27000 standards, to identify the basic security measures to be put in place.
For more advanced risks, the method suggests building realistic attack scenarios. In particular, it takes into account the motivations and resources of potential attackers, in order to identify the system's weak points and define the most appropriate security measures.
EBIOS Risk Manager v1.5, a long-awaited update
After six years of practice and implementation, ANSSI has updated EBIOS Risk manager in March 2024. It is version 1.5.
This version incorporates changes based on feedback from ANSSI and users of the method. The main aim of these changes is to make the method fully compliant with the ISO/CEI 27005:2022 standard.
The main differences compared with the 2018 version concern clarifications to facilitate understanding and clarify certain stages. Another new feature is that the vocabulary used is aligned with ISO terminology.
The benefits of RM EBIOS
This method favours a representative rather than an exhaustive analysis, allowing a rapid adaptation to change the threat context. EBIOS RM offers a clear vision of the ecosystem. It enables the organisation's ecosystem to be mapped and the most threatening stakeholders to be identified. This mapping, combined with the identification of business values and support assets, provides a comprehensive view of the environment in which information systems operate.
RM EBIOS helps identify critical points. Thanks to its strategic and operational scenarios, RM EBIOS makes it easy to identify the most relevant points of entry, propagation relays and exploitation vectors.
ISO 27001 The international standard
ISO/IEC 27001 is an international standard that defines the requirements for implementing an information security management system (WSIS).
It provides a general framework for information security management, including risk management.
Structure and Process
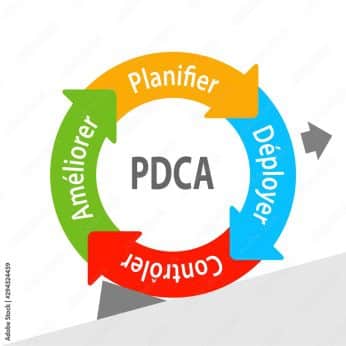
The standard follows a PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle:
- Plan (Plan) Establishing the ISMS by defining the scope, policies, objectives, risk assessment and risk management plan.
- Implement (Do) deploying and applying the defined security measures and controls.
- Check Monitoring and reviewing the performance of the ISMS, in particular through internal audits and management reviews.
- Act Taking corrective and preventive action to continually improve the ISMS.
The benefits of ISO 27001
La ISO 27001 certification is recognised worldwideThe standard provides a structured framework for information security. The standard provides a structured framework For manage information security globally. The PDCA cycle encourages regular re-evaluation and continuous improvement of safety measures.
ISO 27005: focus on risks
ISO 27005 complements ISO 27001 by focusing specifically on information security risk management. It provides a more detailed methodological framework for the identification, assessment and treatment of risks. To this end, it draws on both qualitative and quantitative techniques.
ISO 27005 encourages a flexible and adaptive approach, enabling organisations to choose the most appropriate methods and tools for their specific context.
The benefits of ISO 27005
It offers a detailed methodology for risk analysis, with flexibility of application and complementarity with ISO 27001.
Which method should I choose?
Faced with these three options, what method should you choose to effectively manage cyber security risks? The answer will depend on a number of factors, including :
- The size and complexity of the organisation
- EBIOS The ideal solution for large or complex organisations requiring in-depth risk analysis.
- ISO 27001 Suitable for a wide range of businesses, whether small, medium-sized or large.
- MEHARI : this other risk management method developed by the Club de la Sécurité de l'Information Français (Clusif) is particularly well suited to smaller organisations with a single site and a centralised information system.
- The regulatory context and compliance requirements
- EBIOS RM A benchmark in France, it facilitates compliance with national regulatory requirements.
- ISO 27001 and ISO 27005 internationally recognised, these standards are ideal for companies operating on a global scale or needing to meet international standards.
- Available resources
- ISO 27001 Its implementation may require significant resources in terms of time, staff and budget.
- EBIOS can be applied in a more targeted way, potentially requiring fewer resources.
- MEHARI offers a structured yet accessible approach for organisations with limited resources.
- Safety objectives
- ISO 27001 Information Security Management System (ISMS): recommended if the aim is to implement a complete, certified Information Security Management System (ISMS).
- EBIOS RM and ISO 27005 These are more appropriate if the focus is on analysing and dealing with specific risks.
Conclusion
EBIOS, ISO 27001 and ISO 27005 are complementary rather than competing methodologies.
Many organizations choose to combine these approaches in order to benefit from their respective advantages. For example, a company could use ISO 27001 as the overall framework for its ISMS, incorporate ISO 27005 for its detailed risk analysis methodology, and draw on EBIOS for the development of specific attack scenarios. The key is to choose an approach that matches the needs, resources and culture of the organisation.
Whichever method is chosen, the commitment of management, the active participation of stakeholders and a well-established safety culture with training and training courses are essential. employee awareness are key success factors for effective cyber security risk management.




