The rise of AI in the workplace is revolutionising data protection. personal data : chatbotsproduct recommendations, automatic selection of candidates for recruitment... these AI-based tools raise issues of data confidentiality and security, as well as of bias treatment. And in addition to the RGPDthe entry into force of the recent European regulation on artificial intelligence (AI Act) imposes new legal obligations. How can the Data Protection Officer (DPO) meet these challenges?

Artificial intelligence (AI) is experiencing unprecedented growth. It offers revolutionary possibilities for organisations, but raises a number of concerns about data protection.
In fact, the Data Protection Officer (DPD is at the heart of this challenge. Responsible for implementing European Data Protection Regulation (RGPD) within the organisation to which he has been appointed, he must take account of the new AI law (AI Act, in English) voted by the European Parliament on 13 March 2024.
The DPO's first challenge: assessing data-related risks
AI, and more specifically Generative AI (IAG), are based on the massive exploitation of data to train algorithmic models, the famous major language models (LLM). This collection and processing raises concerns about privacy, informed consent and data security.
Personal data must also comply with the principle of minimization. The CNIL defines it as follows: data must be adequate, relevant and limited to what is necessary for the purposes for which it is processed.
In addition, AI systems can extend or amplify the biases present in training data, thereby threatening the principles of fairness and non-discrimination.
For example, the training data sets used to feed facial recognition systems are mainly made up of portraits of white people. These systems are therefore less likely to recognise people of colour.
DPOs must be vigilant about risks inherent in AI, as :
- Re-identification of individuals from supposedly anonymised data
- The use of sensitive data (gender, ethnic origin, political opinions, etc.) for training models
- Tracking and targeting individuals for behavioural advertising purposes
- Automated decisions with a significant impact on individuals (recruitment, credit, etc.)
Second challenge for the DPO: ensuring RGPD compliance for AI
Beyond the risks, DPOs face operational challenges in ensuring AI systems are compliant with the GDPR. Key challenges include:
– Assessing the necessity and proportionality of data processing for AI systems
– Conducting data protection impact assessments (AIPD) for high-risk treatments
– The implementation of appropriate technical and organisational measures (data protection at the design stage, etc.).
– Managing the rights of data subjects (access, rectification, opposition, etc.) in the context of AI
– Supervision and control of subcontractors involved in the development or use of AI
The AI Act: a new regulatory framework
In response to the challenges posed by AI, the European Union has proposed the AI Act, a regulation aimed at establishing harmonised rules for the development, marketing and use of "reliable" AI systems. This legislative proposal introduces several key concepts that will have a significant impact on the role DPOs.
AI risk classification
The AI Act classifies AI systems into four levels of risk: unacceptable, high, limited and minimal. DPOs will need to be able to identify the level of risk of AI systems used by their organisation and put in place the corresponding requirements.
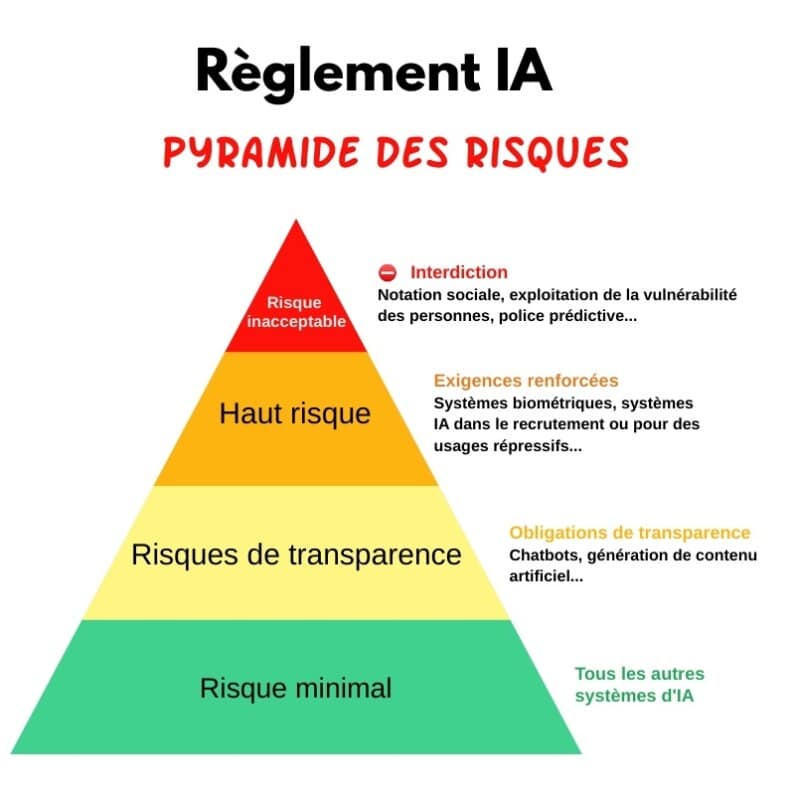
©Alexandre Salque/ORSYS
Requirements for high-risk AI systems
For AI systems considered "high risk", e.g. facial recognition systems, credit rating systems, etc., the AI Act imposes strict requirements throughout the system's lifecycle, such as:
- Carrying out risk assessments and compliance tests
- The implementation of risk management systems and human controls
- Drawing up detailed activity registers
- Designation of a person responsible for monitoring the system's compliance
These requirements will involve close collaboration between DPOs, development teams and AI experts.
Rights of the persons concerned
The AI Act strengthens the rights of individuals by granting them, in particular, the right to be informed when they interact with an AI system and the right to challenge decisions made by these systems. DPOs will have to ensure that these rights are respected and put in place appropriate procedures.
A stronger role for the supervisory authorities
The AI Act gives supervisory authorities (such as data protection authorities) new powers to inspect, monitor and sanction non-compliant AI systems. DPOs will need to work closely with these authorities, including the CNIL, and ensure rigorous documentation of their AI-related activities.
Future prospects for DPOs
With the rise of AI and the emergence of regulations such as the AI Act, the role of DPOs is changing and becoming more strategic than ever. They will be required to work closely with technical, legal and operational teams to integrate data protection and regulatory requirements right from the design and deployment of AI systems.
DPOs will need to develop in-depth expertise in the field of AI, covering technical as well as legal and ethical aspects. They will play a key role in raising awareness and training teams, as well as in promoting a culture of data protection and AI.Responsible AI within their organisation.
In short, DPOs are at the heart of the data protection challenges associated with AI. Their ability to anticipate risks, collaborate with different stakeholders and adapt to regulatory changes will be crucial in enabling their organisation to take full advantage of the benefits of AI while safeguarding the fundamental rights and freedoms of individuals.