Everything can be duplicated: a car, a factory, a human body and even the Earth! As virtual doubles, digital twins enable us to better understand, predict and optimise the real world. Industry, architecture, research and healthcare can no longer do without them. Their advantages are numerous, starting with their cost. For businesses, the virtual world finally has a very real benefit.

The result of advances in 3D, the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence, the digital twin is a promising technology. Industry, urban planning, health and many other fields are using it to speed up innovation. Almost anything can be duplicated. A car to simulate a crash test, a human heart to prepare for surgery, a drug to carry out virtual clinical trials and speed up time to market, a building to facilitate design and improve energy efficiency... Even in IT, digital twins are being used to test software, manage infrastructures or simulate new technologies. cyber attacks.
What is a digital twin?
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a real-world object, system or process. Using 3D modelling technologies, sensors, artificial intelligence and Big Data, these twins can simulate, analyse and predict the behaviour of their real-world counterparts, giving them greater understanding and control over their performance and maintenance.
"While the technology itself is not new - NASA was already using it in the 1960s - the term appeared in industry in the 2000s, with the widespread use of sensors and the analysis of their data," explains Cédric Vasseur, AI specialist and ORSYS trainer.
How do you create them?
The design of a digital twin begins by collecting data on the real object, system or process. Sensors are placed on the object to gather information in real time. 3D models are then created to visually represent its structure and components. Artificial intelligence is then used to analyse the data, to train neural networks via computer codes, and to analyse the results. machine learning to create a model and then simulate the behaviour of the real object using a digital twin.
What are they used for?
While many sectors are reaping the benefits of digital twins, it is industry that has been the driving force.
In industry, the pioneering
A distinction is made between digital product twins and digital production twins. The former are used to design products and validate their performance. They eliminate the need for physical prototypes and reduce development times.
On the other hand digital production twins are used to plan manufacturing, optimise production, monitor supply chains and improve quality. predictive maintenance machines.
Siemens and Nvidia have signed an agreement to facilitate the creation of digital simulations of products and processes.
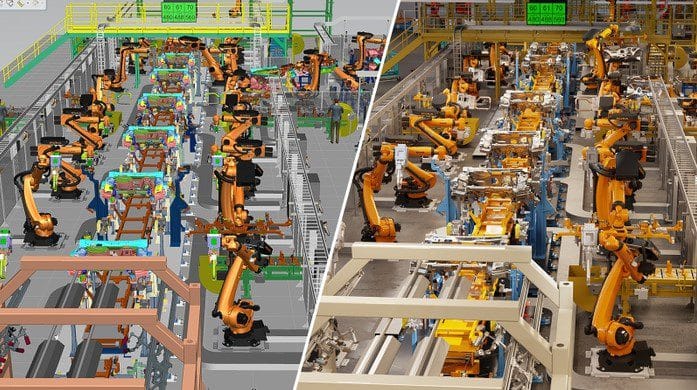
In robotics, this technology is used to design robots. "In the simplest models, we try to ensure that the parts don't collide with each other," explains Cédric Vasseur. "In the most advanced versions, we obtain models that are very close to reality. This is the case with industrial robots.
The use of twins has a practical side in the design of an object: "when you have a development team of 100 people, it's much more practical to work on a digital model than to have 100 people working on a real object" observes Cédric Vasseur. Especially as the digital version benefits from a log of changes made by each member of the development team.
In industry, digital twins are used in aerospace and aeronautics to optimise the design of aircraft, satellites, launchers, etc., reduce costs and improve aircraft reliability and safety.
"These industries use very expensive parts. If something breaks, it will cost more than launching a study on a digital twin," explains Cédric Vasseur.
In other areas
In architecture, we recreate a building from scratch by entering its dimensions into 3D software. Its digital model or BIM (Building Information Modeling) facilitates the design of buildings, improving their energy efficiency and environmental sustainability, in particular by reducing the quantity of materials used.
In town planningSmart cities use digital twins to simulate infrastructure and improve urban mobility.
In healthcare, Digital twins of patients or organs are used to better understand diseases, test treatments or anticipate care needs. Philips has developed a 3D medical tool, Dynamic HeartModel, with which cardiologists monitor the health of patients suffering from cardiovascular disease.
The pharmaceutical industry has also seized on this technology to design drugs more rapidly. The technique is tried and tested: testing virtual drugs on a panel of virtual patients. The result: the duration of clinical trials has been halved!
In ITDigital twins offer a wide variety of applications:
- Software development and testing Simulation and testing of applications in a virtual environment prior to deployment, identifying errors, performance problems and potential problems. vulnerabilities.
- Infrastructure management Virtualisation enables complex infrastructures to be optimised and monitored (data centrenetworks, cloud). This means you can better anticipate resource requirements, improve infrastructure performance and security, and reduce operating costs.
- Cybersecurity simulate and analyse threats in order to improve safety. resilience cyber attacks, testing and countermeasures before they are implemented.
- Training Digital twins: digital twins facilitate learning via virtual learning environments, enabling professionals to train and develop IT skills without having to handle expensive physical hardware or risk damaging real systems.
A promising future
The future of digital twins looks bright, with increasing adoption across many sectors and constant technological advances. Advances in artificial intelligence, virtual and augmented reality, sensors and connectivity will enable the creation of ever more accurate, interactive and useful digital twins.
Training in digital twins is an excellent opportunity for professionals. By mastering the skills needed to design, analyse and manage digital twins, you can make an active contribution to this technological revolution.


