Launched in 2012, the tag management tool in Google's marketing suite, Google Tag Manager (GTM), is certainly not new, but it is often underused. Many companies have deployed it on their websites. And yet, faced with the disappearance of cookies With the increasing importance of third-party data, regulatory constraints on data protection, and the importance of consolidating proprietary data, it seems imperative for businesses to optimise their use of this tool. So what are the benefits of Google Tag Manager? What good practices should companies be implementing? What pitfalls should they avoid? David Lelièvre, digital marketing analytics expert, explains.

La data collection is becoming increasingly complex as a result of the implementation of the general data protection regulation (RGPD) and constantly evolving browser policies. In this context first-party data have become a priority for many companies.
First-party data corresponds to all the data collected by companies directly from their audience (customers, website visitors, followers on social networks, etc.). This data enables companies to better understand the behaviour of their target audiences. Above all, it can be used to refine and personalise campaigns.
Companies are already familiar with a certain type of first-party data via their CRM databases, which centralise information about their customers or prospects. But what about Internet users who have not yet been registered in these databases? Certain information can also be collected using tag management system (TMS) as Google Tag Manager (GTM).
It seems essential for businesses to optimise Google Tag Manager. This tool meets their specific needs in terms of data... and enables them to achieve their marketing objectives. And all the more so since, on 17 July 2023, the issue of hosting data in the United States was clarified and became totally legal.
Google Tag Manager, a solution with multiple benefits
For a number of reasons, Google Tag Manager is a an invaluable asset for maximising the collection of relevant information on a website. This tagging tool has many advantages.
Google Tag Manager is organised around 3 elements:
- the tag that corresponds to the script you want to implement on your site;
- the trigger to define the rule by which you want your script to be triggered (all pages, conversion page, home page, etc.);
- the variables you can use to create your trigger rules and customise your scripts (visitor type, page type, etc.).

1. Simplified management of tracking beacons
Google Tag Manager considerably simplifies the management of tracking tags on a website. These tags, more commonly known as tags, are essential. Google Analytics 4, Facebook, Hotjar, iAdvize... manytools currently used in digital marketing require a tag to operate.
Thanks to GTM and its centralised, remote management of all these tracking tags, it's easy to set up and better manage data collection, greatly reducing the number of actions in the site code while improving the quality and consistency of the data collected.
2. Customised data collection
Google Tag Manager enables you to manage the data needed to optimise your website. The tool enables companies to customise the collection of first-party data in line with their business and marketing objectives.
This enables companies to collect the business data that is most relevant to their activity. This improves their ability to make informed business decisions.
In this way, it is possible, for example, to retarget all visitors who have searched for a "blue" product. Or offer the conversational assistant only to visitors who have spent at least two minutes on a particular section of your site.
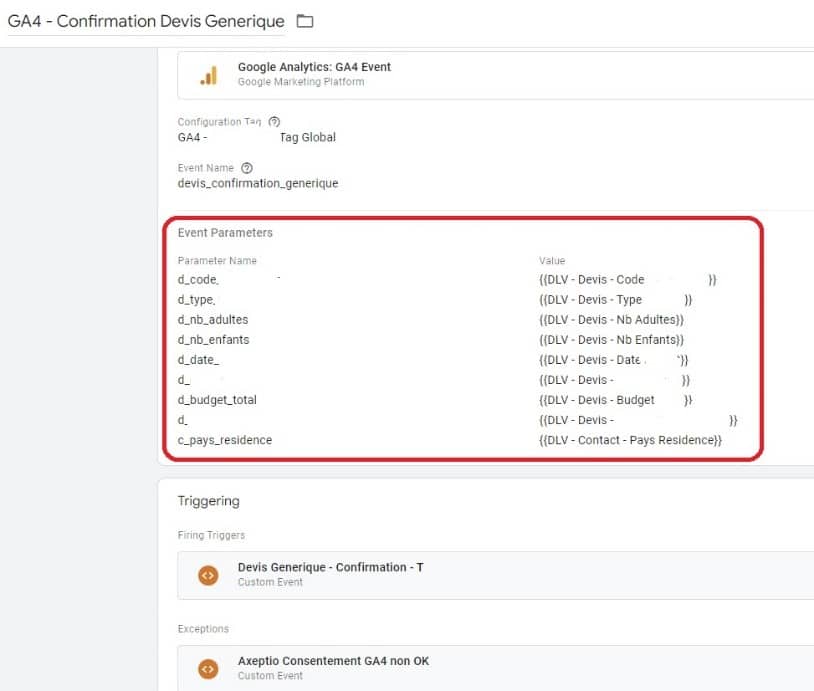
3. Compliance with data protection regulations
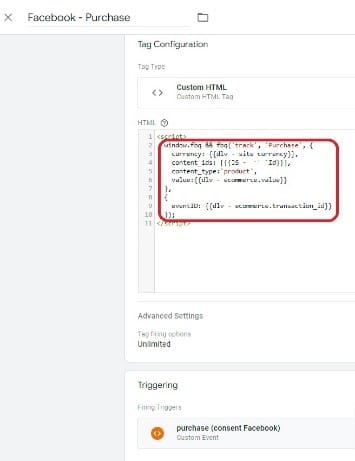
Google Tag Manager allows you to data governance in line with the RGPD. With this and other privacy-related regulations, there is a growing need for transparency and consent when it comes to the collection of user data. Companies using GTM therefore need to ensure that they are compliant with these regulations. But this can add complexity to implementation.
Companies must therefore ensure that the tags they set up via GTM comply with these directives. This applies in particular to the collection of consent.
Server-side implementation means that tags are hosted on the company's own IT servers. In this way, this implementation contributes to the reappropriation of data flow processes. For example, it enables better control of the information sent to the various partners (Google Ads, Facebook Ads...).
What is the RGPD?
These regulations aim to protect the privacy of individuals by imposing strict rules on the collection and processing of personal data. personal databy guaranteeing transparency and granting rights to the people concerned.
The RGPD is based on 3 pillars:
- Protection of personal data. The GDPR aims to protect individuals' personal data by imposing strict rules on how organisations collect, store and process this data. Personal data includes information such as names, addresses, telephone numbers and email addresses.
- Consent and transparency. Companies must obtain the explicit consent of individuals before collecting their personal data. In addition, they must inform individuals of how their data will be used. Individuals have the right to know what data is held about them.
- Individuals' rights. The GDPR grants individuals a number of rights, including the right to access their data, rectify it, delete it and object to its use. Companies must also put security measures in place to protect this data.
[ Read also ]
White paper : RGPD and artificial intelligence: what impact on the marketing function?
Beware of the classic implementation pitfalls
Google Tag Manager offers a wide range of possibilities for collecting information. However, there are a number of factors that need to be taken into account when using this tool, in order to avoid pitfalls.
Weak marketing thinking
The implementation of the tool must be supported by marketing thinking. No unnecessary information should be collected. Concentrate on activating tags and events that enable you to create added value for web users or for your campaigns.
Technical complexity
GTM makes it easy for marketers to set up tags. But there can be technical complexities in ensuring that everything is set up correctly and doesn't break other parts of a website. This often requires close collaboration between web developers and marketers.
Performance problems
Adding a large number of tags and scripts can potentially slow down the performance of a website. Regular monitoring of speed and performance is crucial to avoid degrading the user experience.
Constantly evolving technology
With technology constantly evolving, companies need to ensure they stay up to date with the latest GTM features and best practices. This requires ongoing training and regular updating of skills.
Tag management
Without good management, it's easy to end up with a lot of obsolete or unused tags in GTM. This can make it difficult to track and manage what's active and what's not.
Competition
Other tag management platforms may offer specific features or benefits that GTM does not, leading some companies to consider other options.
What steps can you take to audit your implementation of the tool?
Once you've avoided the pitfalls, you need to adopt a methodical approach and follow these 6 steps.
Stage 1 :define the useful data to be collected
Data collection should be the result of prior marketing and business thinking. For example, will this data enable you to :
- better understand the customer journey on your site?
- personalise visitors' journeys?
- set up new campaign scenarios?
Step 2 :define collection specifications
Can this data be retrieved? How can it be retrieved?
Following an audit, this 2nd stage will validate the possibility of recovering the data and specify reliable data collection rules.
Google Tag Manager offers a number of ways to extract relevant data:
- retrieve the information stored in your internal cookies ;
- decompose your URLs to recover the different levels of the tree structure of your site or the parameters of requests ;
- retrieve the JavaScript variables used to develop your site ;
- or, indirectly this time, integrate a custom script with the help of a developer.
Step 3 :activate data in your digital solutions
The data may be used in various ways. These include
- as personalised analysis variables in Google Analytics. For example, do users only read recently published content? Do they read content by a particular author?
- as a trigger for your various tools. For example, you could offer an online questionnaire to web users identified as the best customers, to better understand their behaviour;
- as a segmentation criterion to better target your advertising. For example, you can target only those people who have visited more than three product pages without making a purchase.
Step 4 :ensure data compliance

Make sure that all the data you collect complies with current regulations such as the RGPD.
Use pop-ups or banners to obtain users' consent before collecting their data.
Step 5: Continuous testing and optimisation
Use GTM's preview environment to test new tags before deploying them on the live site. Regularly monitor your site's performance to ensure that GTM tags do not negatively affect speed or functionality. Periodically review active tags to identify those that are no longer required or need to be updated.
Step 6:training and updating skills
Make sure that your team is well trained in the use of GTM and is aware of best practices and recent developments. Encourage ongoing training and certification to ensure optimal use of the tool.
Testimonial
"Google Tag Manager frees marketing from technology.
Anne-Laure, Marketing Manager
Training to become more autonomous in tracking our website
It all started with the "Google Analytics (GA4), analysing your website statistics" training course. The marketing team took this course to learn about the new features offered by the tool. The training also gave us the desire to gain greater autonomy over the tracking of our websites, which until then had been the preserve of the development team. So we asked for an in-house training session dedicated to Google Tag Manager, the Google tool for site tagging. We invited our web developer to this session. The first objective was to create greater cohesion between the marketing and technical teams. The second objective was to give the marketing team total control over the tool and enable them to make their own settings in GTM - a first!
The GTM tool for greater efficiency
The GTM training enabled us to understand the structure of the tool, its operating logic and the operational techniques for using it. And the results are there: the tool allows us to obtain personalised and more detailed tracking statistics. This training opens up a whole new world of possibilities. As a bonus, the trainer provided us with tagging plan templates to help us structure our reporting. He also advised us on nomenclature logic to facilitate collaborative work and make our analyses faster and more intuitive!
A subject for exploration
During the course, we worked on practical cases using our own data... it was very practical! And, a month after the course, we were able to have a video chat with the trainer to learn from our initial experiences. Mission accomplished: by making us self-sufficient in tracking, this training enabled us to enrich our new reports and structure them better. We still have a long way to go, but we now have the tools and know-how to move forward!
Key facts: mastering Google Tag Manager is essential for businesses looking to optimise their customer data collection and improve their digital marketing. However, making the most of this tool requires a considered approach based on compliance, training and continuous improvement. By adopting a methodical approach and avoiding common pitfalls, businesses can make the most of GTM to meet their specific data needs and achieve their marketing objectives.





