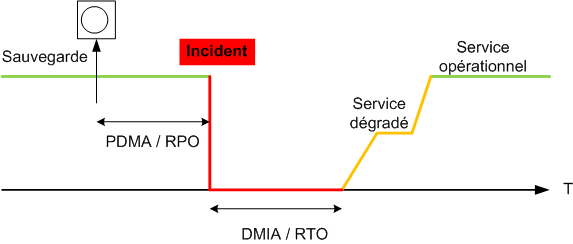
The RPO (Recovery Point Objective) represents the maximum acceptable time interval between two data backups.
In other words, it is the the maximum amount of data a company can afford to lose in the event of a major incident, such as a server breakdown, fire, or cyber attack.
It is defined as part of the Disaster Recovery Plan (PRA) and cyber strategy.resilience of a company.
Key features of the RPO
- Data freshness RPO: determines the freshness of the data to be restored in the event of an interruption.
- Backup objective It defines the company's objectives and safeguarding strategy..
- Time measurement RPO is generally expressed in units of time (hours, minutes)..
- Customisation RPO can vary depending on the systems and types of data within a company..
Importance of RPO
RPO is crucial for :
- Minimise the risk of data loss
- Maintaining data integrity
- Preserving the trust of customers and partners
A concrete example
If a company defines an RPO of 4 hours, this means that data must be backed up at least every 4 hours. So, in the event of an incident, the maximum loss of data would be limited to 4 working hours.
- A bank: an RPO of 15 minutes means that the bank cannot afford to lose more than 15 minutes of transactions in the event of a breakdown.
- A hospital: an RPO of 1 hour may be acceptable for certain administrative data, but an RPO of a few minutes is essential for medical records.
Relationship with the RTO
Although distinct, the RPO and the RTO (Recovery Time Objective) are complementary in the disaster recovery strategy. Together, they determine the total downtime of a resource after a major incident, and influence investment in the following areas computer security.
RTO = Recovery Time Objective
RPO =Recovery Point Objective PDMA=Data Loss Maximum Allowable
DMIA = Maximum Admissible Interruption Duration